Welcome to the world of business inventory programs, where the efficient management of stock and supplies empowers businesses to thrive. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of inventory management, exploring its multifaceted role in driving business success.
From the fundamental concepts of inventory management systems to the latest advancements in inventory optimization techniques, this guide equips you with the knowledge and insights necessary to optimize your inventory operations, minimize costs, and maximize profits.
Inventory Management Systems
Inventory management systems (IMS) are software applications designed to help businesses track and manage their inventory levels, from raw materials to finished goods. They provide real-time visibility into inventory levels, allowing businesses to make informed decisions about purchasing, production, and distribution.
Implementing an IMS can provide numerous benefits for businesses, including:
- Improved inventory accuracy and reduced shrinkage.
- Optimized inventory levels, reducing the risk of stockouts and overstocking.
- Increased efficiency in inventory management processes, saving time and resources.
- Enhanced collaboration and communication among different departments involved in inventory management.
- Improved customer satisfaction by ensuring product availability and reducing lead times.
Types of Inventory Management Systems
There are various types of IMS available, each tailored to specific business needs. Some common types include:
- Periodic Inventory Systems: These systems require manual inventory counts at regular intervals, typically monthly or quarterly.
- Perpetual Inventory Systems: These systems track inventory levels continuously, updating them with each transaction.
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory Systems: These systems aim to minimize inventory levels by ordering and receiving materials only when needed for production.
- Warehouse Management Systems (WMS): These systems are designed specifically for managing inventory in warehouses, providing advanced features for tracking, storage, and retrieval.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems: These comprehensive systems integrate inventory management with other business functions, such as accounting, sales, and production.
Inventory Control
Inventory control is a crucial aspect of business operations that ensures optimal stock levels, minimizing losses due to overstocking or understocking. Effective inventory control helps businesses maintain efficient cash flow, reduce waste, and improve customer satisfaction.
Methods of Inventory Control
There are various methods of inventory control, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Some common methods include:
- First-In, First-Out (FIFO): This method assumes that the oldest inventory items are sold first. It is often used for perishable goods to prevent spoilage.
- Last-In, First-Out (LIFO): This method assumes that the most recently acquired inventory items are sold first. It can be beneficial during periods of inflation, as it reduces the cost of goods sold.
- Weighted Average Cost: This method calculates the average cost of inventory items based on their purchase prices. It provides a more stable cost of goods sold compared to FIFO or LIFO.
Inventory Control Techniques
Businesses can implement various inventory control techniques to optimize their stock levels. Some common techniques include:
- Cycle counting: This involves periodically counting inventory items to ensure accuracy and identify any discrepancies.
- Just-in-time (JIT) inventory: This technique aims to minimize inventory levels by ordering only what is needed, when it is needed.
- Safety stock: This is an additional inventory buffer maintained to mitigate the risk of stockouts due to unexpected demand or supply chain disruptions.
Inventory Optimization
Inventory optimization is a crucial aspect of business operations, ensuring the right amount of inventory is available to meet customer demand while minimizing costs and risks.
It involves managing inventory levels to maximize efficiency, reduce waste, and improve profitability.
Benefits of Inventory Optimization
- Reduced inventory costs by minimizing excess stock and spoilage.
- Improved customer satisfaction by ensuring product availability and reducing lead times.
- Enhanced operational efficiency by streamlining inventory management processes.
- Increased profitability by optimizing inventory levels to maximize sales and minimize holding costs.
Inventory Optimization Techniques
- ABC Analysis: Categorizing inventory items based on their value and usage, allowing for targeted management.
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory: Maintaining minimal inventory levels and replenishing as needed, reducing holding costs and improving cash flow.
- Economic Order Quantity (EOQ): Determining the optimal quantity to order at a time to minimize total inventory costs.
- Safety Stock: Maintaining a buffer of inventory to protect against unexpected demand or supply disruptions.
- Inventory Tracking Software: Utilizing technology to monitor inventory levels, automate reordering, and optimize stock levels.
Inventory Forecasting
Inventory forecasting is the process of predicting future demand for inventory items. It is a critical part of inventory management, as it helps businesses ensure that they have the right amount of inventory on hand to meet customer demand without overstocking or running out of stock.
There are a number of different inventory forecasting methods, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Some of the most common methods include:
Time Series Forecasting
- Moving averages: This method takes the average of past demand over a specific period of time to forecast future demand.
- Exponential smoothing: This method weights past demand more heavily than older demand, giving more importance to recent trends.
- Seasonal decomposition of time series: This method decomposes demand into its seasonal, trend, and residual components, which can then be used to forecast future demand.
Causal Forecasting
- Regression analysis: This method uses historical data to build a statistical model that can be used to predict future demand.
- Econometric models: These models use economic data to forecast future demand.
Judgmental Forecasting
- Expert opinion: This method involves asking experts to forecast future demand.
- Customer surveys: This method involves surveying customers to gauge their future demand.
The best inventory forecasting method for a particular business will depend on the nature of the business, the products it sells, and the availability of data.
Inventory Replenishment
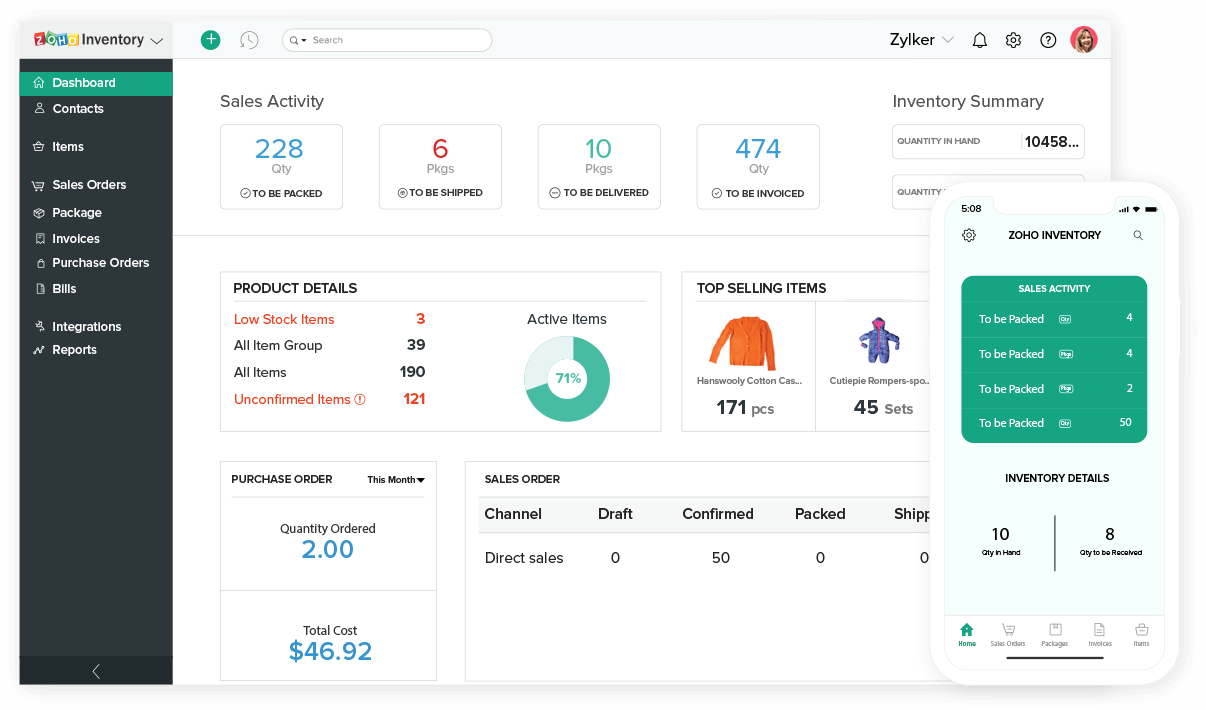
Inventory replenishment refers to the process of restocking inventory to maintain optimal levels to meet customer demand. It plays a crucial role in business operations, ensuring uninterrupted supply and minimizing the risk of stockouts or overstocking.
Inventory Replenishment Strategies
Various inventory replenishment strategies exist, each tailored to specific business needs and inventory characteristics:
- Fixed-Time Replenishment: Replenishment occurs at predetermined intervals, regardless of inventory levels.
- Fixed-Order-Quantity Replenishment: A fixed quantity is ordered each time inventory falls below a specified reorder point.
- Periodic Review Replenishment: Inventory levels are reviewed periodically, and replenishment orders are placed based on the difference between actual and desired inventory levels.
- Min-Max Replenishment: Inventory is replenished when it reaches a minimum threshold (min) and stops when it reaches a maximum threshold (max).
Inventory Replenishment Techniques
To implement inventory replenishment strategies effectively, businesses can utilize various techniques:
- Demand Forecasting: Predicting future demand helps determine the optimal quantity and timing of replenishment.
- Lead Time Management: Tracking and optimizing lead times ensures timely delivery of replenishment orders.
- Safety Stock: Maintaining a buffer stock helps mitigate uncertainties in demand and lead times.
- Inventory Monitoring: Regular monitoring of inventory levels and usage patterns provides insights for informed replenishment decisions.
- Vendor Management: Collaborating with vendors to establish efficient and reliable replenishment processes.
Inventory Valuation

Inventory valuation is the process of determining the monetary value of the inventory on hand. It is an important aspect of business because it affects the financial statements, including the balance sheet and income statement. The inventory valuation method used can also impact the company’s tax liability.
There are different inventory valuation methods that can be used, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Some of the most common methods include:
First-In, First-Out (FIFO)
- Assumes that the first inventory purchased is the first inventory sold.
- This method results in a higher cost of goods sold (COGS) and a lower ending inventory value during periods of rising prices.
Last-In, First-Out (LIFO)
- Assumes that the last inventory purchased is the first inventory sold.
- This method results in a lower COGS and a higher ending inventory value during periods of rising prices.
Weighted Average Cost (WAC)
- Calculates the average cost of the inventory on hand by dividing the total cost of the inventory by the total number of units on hand.
- This method results in a COGS and ending inventory value that is in between the FIFO and LIFO methods.
The choice of inventory valuation method depends on a number of factors, including the nature of the business, the industry in which the business operates, and the tax implications. It is important to choose a method that is appropriate for the business and that will provide accurate financial information.
Inventory Performance Metrics
Inventory performance metrics are essential for businesses to track and measure the efficiency and effectiveness of their inventory management practices. They provide valuable insights into inventory levels, turnover, and overall performance, enabling businesses to identify areas for improvement and optimize their inventory operations.
Different inventory performance metrics can be used to assess various aspects of inventory management, including:
Inventory Turnover Ratio
The inventory turnover ratio measures how efficiently a business is using its inventory. It is calculated by dividing the cost of goods sold (COGS) by the average inventory value over a period of time. A higher inventory turnover ratio indicates that the business is effectively managing its inventory and not holding on to excess stock.
Days Sales of Inventory (DSI)
DSI measures the average number of days it takes a business to sell its inventory. It is calculated by dividing the average inventory value by the daily COGS. A shorter DSI indicates that the business is selling its inventory quickly and not tying up capital in excess stock.
Inventory Accuracy
Inventory accuracy refers to the degree to which the physical inventory matches the records. It is important for businesses to maintain high inventory accuracy to ensure that they have the right amount of stock on hand and to avoid stockouts or overstocking.
Stockout Rate
The stockout rate measures the percentage of customer orders that cannot be fulfilled due to lack of inventory. A high stockout rate can lead to lost sales and customer dissatisfaction.
Inventory Holding Costs
Inventory holding costs represent the expenses associated with storing and maintaining inventory, such as warehousing, insurance, and opportunity cost. Businesses should strive to minimize inventory holding costs while maintaining adequate stock levels to meet customer demand.
Inventory Management Software
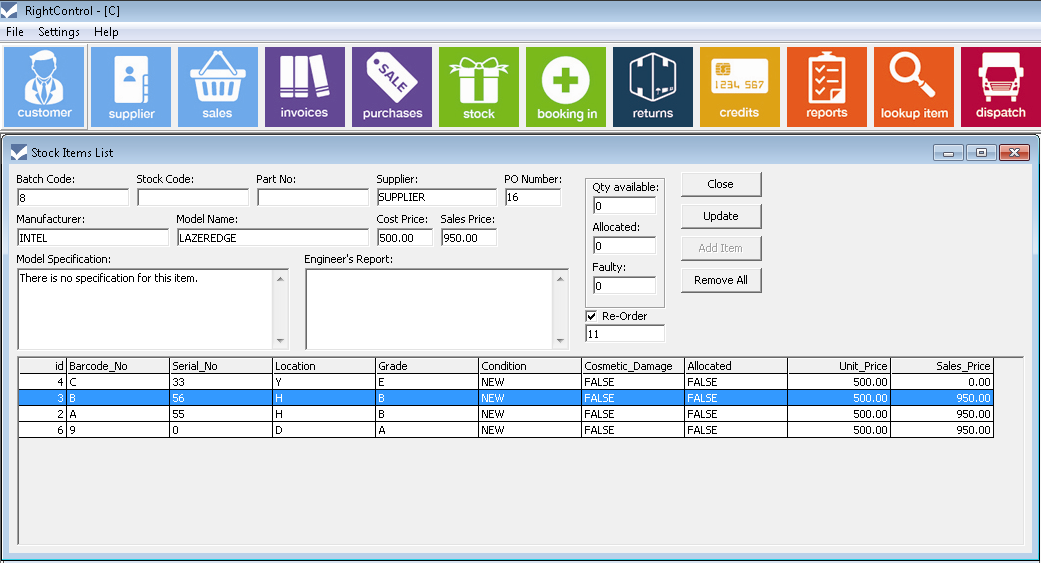
Inventory management software is a crucial tool for businesses to efficiently track, manage, and optimize their inventory levels. It provides real-time visibility into inventory data, enabling businesses to make informed decisions regarding stock levels, reordering, and overall inventory management strategies.
There are various types of inventory management software available, each tailored to specific business needs and industries. Some common types include:
Cloud-Based Inventory Management Software
Cloud-based inventory management software is hosted on remote servers, allowing businesses to access their inventory data from anywhere with an internet connection. This type of software is often cost-effective and scalable, making it suitable for businesses of all sizes.
On-Premise Inventory Management Software
On-premise inventory management software is installed on the business’s own servers, providing greater control and customization options. This type of software is typically more expensive and requires dedicated IT resources for maintenance and updates.
Perpetual Inventory Management Software, Business inventory program
Perpetual inventory management software continuously updates inventory records as transactions occur. This provides real-time visibility into inventory levels, reducing the risk of overstocking or understocking.
Periodic Inventory Management Software
Periodic inventory management software updates inventory records at specific intervals, such as monthly or quarterly. This type of software is less expensive and easier to implement but does not provide real-time visibility into inventory levels.
Examples of Inventory Management Software
Some popular examples of inventory management software include:
- SAP Business One
- NetSuite
- Oracle NetSuite
- Fishbowl Inventory
- QuickBooks Commerce
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, business inventory programs are indispensable tools for businesses of all sizes, providing a wealth of benefits that enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and drive growth. By embracing the principles and practices Artikeld in this guide, you can unlock the full potential of your inventory management system and empower your business to achieve new heights of success.
FAQ Overview: Business Inventory Program
What is the primary purpose of a business inventory program?
A business inventory program is designed to help businesses track, manage, and optimize their inventory levels, ensuring that they have the right amount of stock to meet customer demand while minimizing waste and storage costs.
How can inventory optimization techniques benefit my business?
Inventory optimization techniques can help businesses reduce inventory holding costs, improve cash flow, minimize stockouts, and increase customer satisfaction by ensuring that the right products are available at the right time and in the right quantity.
What are the different types of inventory management systems available?
There are various types of inventory management systems available, including perpetual inventory systems, periodic inventory systems, and hybrid inventory systems. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the best choice for a particular business depends on its specific needs and requirements.